Want to achieve the MMCC-approved benefits of medicinal cannabis in an odor-free, cost-effective way? Then a cannabis extract may be right for you. The process of cannabis extraction allows for the creation of medicinal grade cannabis products in versatile forms such as waxes, oils, and distillates.
Cannabis extracts are often more potent than flower, making them a more economically efficient choice for some medicinal users. They also allow users to consume cannabis without the odor, taste, and strong smell of cannabis smoke. Individuals with sensitive lungs (or those who simply don’t like smoking) may benefit more from cannabis extracts.
So how does this process work, and how can you make an informed decision about purchasing products made by cannabis extraction? Let’s find out!
The cannabis extraction process
The cannabis plant contains over 500 compounds, including compounds called terpenes and cannabinoids. Cannabis extraction separates cannabinoids and terpenes from inactive compounds , resulting in a “cleaner” and “purer” form of cannabis than simply smoking whole flower.
The extraction process is highly complex and can also increase the potency of the cannabis. Many patients report stronger mental effects while using cannabis extracts (also known as cannabis concentrates) as compared to other forms of cannabis.
A cannabis extract is also more cost-efficient for the user. The effects from a cannabis extract may also last longer yet require a significantly smaller amount. Many types of extracts also stay fresher and retain their potency for a longer period of time when properly stored.
The four most common methods of cannabis extraction include:
1. Solvent-free extraction
Most solventless extraction processes start with water and ice. The entire plant (frozen or dry) is placed into a cold-water bath and agitated, which separates the trichomes from the plant material. Micron mesh bags are used to separate the flower material from the water/trichome solution. From there, the extracted wet material is placed into a freeze dryer and the water is removed via sublimation. The dry trichomes (bubble hash) looks like sand and can be smoked as is, or pressed to extract the oil from the cuticle. Next, smaller micron mesh bags are filled with flower, bubble hash, or dry sift (kief). Those micron bags are then placed between two steel plates, where heat and pressure extract the oil . This oil is similar to shatter and budder, but can also be isolated THCA or terpene cartridges.
2. Ethanol or alcohol extraction
Ethanol extraction, also known as ethyl alcohol extraction, uses a colorless and flammable liquid that can produce intoxication, be used for fuel, and also used as a solvent. . Ethanol extraction can be performed under warm or cold temperatures. Generally, raw and ground-up cannabis material (dry) is soaked in pre-chilled ethanol for a certain amount of time, which dissolves the desired cannabinoids and terpenes from the plant matter. After the initial extraction process, the solution is filtered, or spun and the ethanol is purged from the extract. Post-processing techniques gently remove ethanol from the extracts through evaporation. Ethanol may be removed and reused with rotary evaporators, falling film evaporators, or a vacuum distillation system.
If further refinement is desired, impurities such as plant lipids, chlorophyll, waxes, and fats can be removed from the oil via winterization. Chilling the oil and ethanol solution can cause these undesirable compounds to separate (precipitate) and rise to the top for easier removal. The cooling process can be performed in freezers, cold rooms, or other cooling equipment.
3. CO2 cannabis extraction
CO2 is a powerful solvent. Under pressure, at room temperatures, and under normal pressures it is a colorless, odorless gas. Because CO2 is not naturally a liquid in regular temperatures and pressures, it is not capable of being used as an extraction solvent without some alteration. In order to do this, pressure and temperature must be manipulated to very specific variables so that it reaches a liquid form.Once this point has been reached, CO2 is no longer in its gaseous state and converts into a supercritical fluid. At this point, the supercritical CO2 acts similar to a liquid solvent such as ethanol. It is then capable of saturating the cannabis biomass and stripping plant compounds from the material before being evaporated off and recycled for reuse.
4. Butane or propane (hydrocarbon) extraction
BHO or PHO extraction, often referred to as hydrocarbon extraction, is broadly used to produce high-potency terpene rich cannabis extracts. In this type of extraction, butane, or propane (instrument or medical grade) is used in its liquid form, which means a specific temperature and pressure must be maintained. The liquid butane/propane is washed over the raw plant, dissolving desirable components including cannabinoids and terpenes. As propane has an even lower boiling point than butane, it is often used to strip additional compounds, such as terpenes. The solution is then deposited in the collection vessel and the solvent is removed to leave the extract, which may go through post-processing to achieve the desired final product.
It’s important to note that many types of solvent-based extractions are complex and, for best results, should only be attempted by licensed professionals. In addition to being dangerous, making your own extracts is illegal in many states.
Types of extract
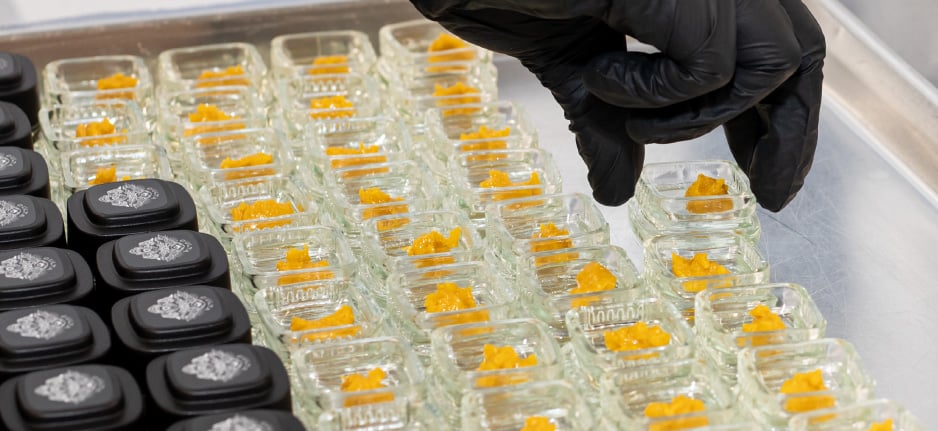
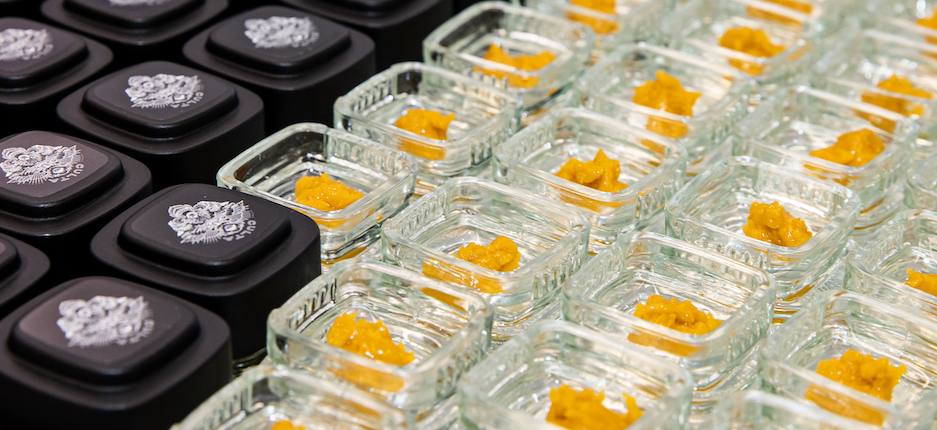
The cannabis extraction process can result in numerous types of extract, also known as cannabis concentrate. Some of the most popular forms of cannabis extract include:
Crude Oil
Cannabis crude oil is a type of extract created with a solvent using either fresh or frozen cured flower. Cannabis crude oil is rarely used on its own, however it can be further processed into a wide variety of consumer-grade medicinal cannabis extracts.
Live Resin
Live resin products are made by extracting whole plant cannabis flower that is freshly frozen after harvesting in a closed loop extraction system. By using frozen cannabis material, the finished product has robust, exceptional terpene and cannabinoid profiles that resemble the qualities of the live plant. Live resin ranges in color from light amber to yellow gold and has a moist, shiny looking exterior with a strong, rich smell. Live resin has many different consistencies and naming conventions. For example, live sugar is a form of high potency live resin that looks like a light yellow to bright orange sugar scrub, while live resin badder is a smoother, more malleable consistency (resembling cake badder or creamy peanut butter) with lower potency and higher terpene profiles.
Wax
Also referred to as crumble or honeycomb, wax is made the same way other concentrates are made with cured flower or bud material from the cannabis plant. Hydrocarbon solvent, such as butane, is introduced to the plant material to remove the plant’s resin using a closed loop extraction system. The resulting oil is heated at low temperatures and whipped vigorously to remove all residual solvent. Wax is generally drier and crumblier than its counterpart budder.
Budder
Budder is wax with higher moisture content. The consistency of budder is oily and malleable. Budder contains a higher moisture content because it is whipped less than wax. Because the product is whipped by hand, it gains airy peaks that are similar to whipped topping or creamy peanut budder. This product normally uses cured flower as the input ingredient.
Shatter
Shatter gets its name from its hard, glass-like consistency. This cannabis concentrate contains between 70-80% cannabinoid potency. The process of making shatter starts with dried and cured cannabis flower that is run through a closed loop extraction system and spread thin onto parchment. It is vacuumed purged with heat to remove the residual hydrocarbon solvent and allowed to cool and harden.
Cannabis distillate
Distillate is a cannabis extract usually created using ethanol or hydrocarbon extracted oil. Starting with an extracted oil, specific heat is applied until the desired ingredient evaporates based on its boiling point. When the vapors cool it condenses back into a liquid, separated from unwanted additives or impurities. This final product is a pure and potent cannabis oil that tests at around 80-90% + THC.
THCA crystalline
THCA crystalline is a highly refined form of cannabis oil and one of the most potent forms of THC. The resulting isolate is nearly clear and resembles crystals. Making THC crystalline is often called “diamond mining,” because THCA naturally forms into crystals, and it can start to look like tiny diamonds. As the cannabinoid crystals form, the terpenes, on the other hand, are pushed-out into a liquid layer. The crystals are THCA and the syrupy liquid is rich in terpenes and low levels of cannabinoids. The two are often separated but can be used together as well.
Rosin
Rosin is sometimes referred to as solventless hash oil (SHO) because it’s made without solvents. There are many types of rosin, including flower, hash, sift and live. Flower rosin is made by pressing dried and cured cannabis flower in a micron bag in order to ensure optimal quality and remove excess moisture before pressing. Hash rosin is made by pressing ice water hash. Because the starting material has already been concentrated to remove biomass, the transition from ice water hash to rosin can result in an especially pure and potent product- the gold standard for solventless extraction. In some cases, pure hash rosin products can reach up to 90% THC or even 99% if THCA separation is used.
THC isn’t everything, though -- some of the best and most flavorful hash rosin can test at 50-60% and have an excellent terpene profile. Sift rosin is made using dry sift hashish or kief. It is generally less potent than hash rosin and more potent than flower rosin. Live rosin is considered to be the ultimate solventless extract. It is created using fresh frozen cannabis that goes through ice water extraction, after which the ice water hash can then be further processed using a rosin press. The result is a creamy extract that has a robust flavor profile and is light in color.
Find high-quality cannabis extracts at CULTA
Whether you’re new to cannabis extractions or have been using medicinal cannabis products for years, CULTA can help you find the best product for your needs. Visit our Baltimore dispensary to discuss extracts with one of our friendly budtenders, or brush up on the basics by reading our Dabbing Basics: FAQs.